- Load the r packages we will use
- download CO2 emissions per capita from Our World in Data into the directory for this post.
3.) assign the location of the file to ‘file_csv’. The data should be in the same directory as the file
read the data into r and assign it to emissions
file_csv <- here("_posts",
"2021-02-26-reading-and-writting-data",
"co-emissions-per-capita.csv")
emissions <- read_csv(file_csv)
- Show the first 10 rows( observations of)
emissions
emissions
# A tibble: 22,383 x 4
Entity Code Year `Per capita CO2 emissions`
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Afghanistan AFG 1949 0.00191
2 Afghanistan AFG 1950 0.0109
3 Afghanistan AFG 1951 0.0117
4 Afghanistan AFG 1952 0.0115
5 Afghanistan AFG 1953 0.0132
6 Afghanistan AFG 1954 0.0130
7 Afghanistan AFG 1955 0.0186
8 Afghanistan AFG 1956 0.0218
9 Afghanistan AFG 1957 0.0343
10 Afghanistan AFG 1958 0.0380
# ... with 22,373 more rowstidy_emissions <- emissions%>%
clean_names()
tidy_emissions
# A tibble: 22,383 x 4
entity code year per_capita_co2_emissions
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Afghanistan AFG 1949 0.00191
2 Afghanistan AFG 1950 0.0109
3 Afghanistan AFG 1951 0.0117
4 Afghanistan AFG 1952 0.0115
5 Afghanistan AFG 1953 0.0132
6 Afghanistan AFG 1954 0.0130
7 Afghanistan AFG 1955 0.0186
8 Afghanistan AFG 1956 0.0218
9 Afghanistan AFG 1957 0.0343
10 Afghanistan AFG 1958 0.0380
# ... with 22,373 more rows6.) Start with the tidy_emissions THEN use filter to extract rows year == 1994 THEN use skim to calculate the descriptive statistics
| Name | Piped data |
| Number of rows | 219 |
| Number of columns | 4 |
| _______________________ | |
| Column type frequency: | |
| character | 2 |
| numeric | 2 |
| ________________________ | |
| Group variables | None |
Variable type: character
| skim_variable | n_missing | complete_rate | min | max | empty | n_unique | whitespace |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entity | 0 | 1.00 | 4 | 32 | 0 | 219 | 0 |
| code | 12 | 0.95 | 3 | 8 | 0 | 207 | 0 |
Variable type: numeric
| skim_variable | n_missing | complete_rate | mean | sd | p0 | p25 | p50 | p75 | p100 | hist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| year | 0 | 1 | 1994.00 | 0.00 | 1994.00 | 1994.00 | 1994.00 | 1994.00 | 1994.00 | ▁▁▇▁▁ |
| per_capita_co2_emissions | 0 | 1 | 4.89 | 6.82 | 0.02 | 0.56 | 2.66 | 7.26 | 60.56 | ▇▁▁▁▁ |
7.)13 observations have a missing code. How are these observations different? Start with tidy_emissions then extract rows with year == 1994 and are missing a code.
# A tibble: 12 x 4
entity code year per_capita_co2_emissions
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Africa <NA> 1994 1.04
2 Asia <NA> 1994 2.27
3 Asia (excl. China & India) <NA> 1994 3.23
4 EU-27 <NA> 1994 8.48
5 EU-28 <NA> 1994 8.66
6 Europe <NA> 1994 8.87
7 Europe (excl. EU-27) <NA> 1994 9.36
8 Europe (excl. EU-28) <NA> 1994 9.22
9 North America <NA> 1994 14.1
10 North America (excl. USA) <NA> 1994 4.98
11 Oceania <NA> 1994 11.5
12 South America <NA> 1994 2.06Step 8 Start with tidy_emissions THEN use filter to extract rows with year == 2019 and without missing codes THEN USE SELECT TO DROP the year variable THEN USE RENAME TO CHANGE THE VARIABLE ENTITY TO COUNTRY ASSIGN THE output to emissions_2019
emissions_2019 <- tidy_emissions %>%
filter(year== 1994, !is.na(code))%>%
select(-year) %>%
rename(country =entity)
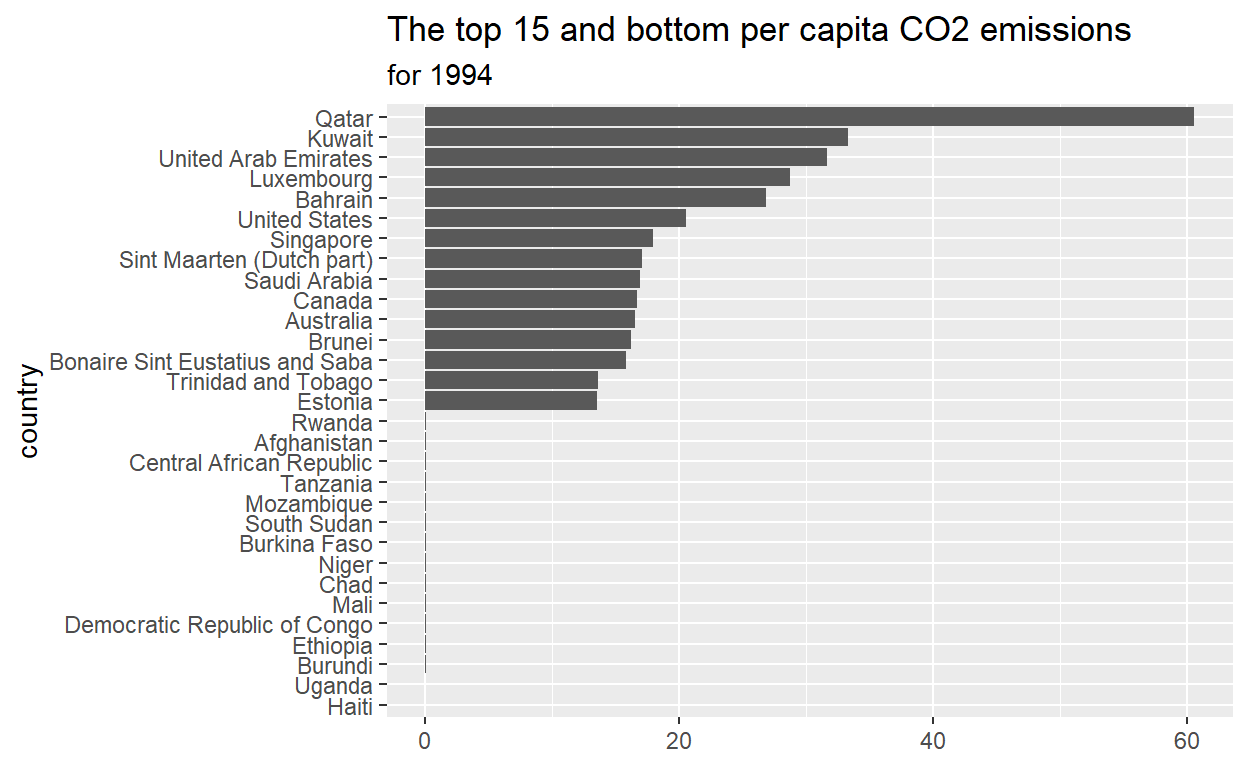
9.) Which countries have the highest per_capita_c02_emissions ?
max_15_emitters <- emissions_2019 %>%
slice_max(per_capita_co2_emissions, n=15)
10.) Which countries have the lowest per_capita_co2_emissions ?
- start with
emissions_2019then - use
slice_minto extract the 15 rows with the lowest values - assign the output to
min_15_emitters
min_15_emitters <- emissions_2019 %>%
slice_min(per_capita_co2_emissions, n=15)
11.) use bind_rows to bind together the max_15_emitters -assign the output to max_15_emitters
max_min_15 <- bind_rows(max_15_emitters,min_15_emitters)
- Export
max_min_15to 3 file formats
max_min_15 %>% write_csv("max_min_15.csv")#comma seperated values
max_min_15 %>% write_tsv("max_min_15.tsv") # tab seperated
max_min_15 %>% write_delim("max_min_15.psv", delim = "|")# pipe-seperated
13.) REad the 3 files into r format
max_min_15_csv <- read_csv("max_min_15.csv")
max_min_15_tsv <- read_tsv("max_min_15.tsv")
max_min_15_psv <- read_delim("max_min_15.psv", delim = "|")
14.) use setdif to check for any differences among max_min_15_csv
setdiff(max_min_15_csv,max_min_15_tsv, max_min_15_psv)
# A tibble: 0 x 3
# ... with 3 variables: country <chr>, code <chr>,
# per_capita_co2_emissions <dbl>15.) reorder country in max_min_15 for plotting and assign to max_min_15_plot_data start with emissions_2019 THEN use mutate to reorder country according to `per_capita
max_min_15_plot_data <- max_min_15 %>%
mutate(country =reorder (country, per_capita_co2_emissions))
16.) plot max_min_15_data
ggplot(data =max_min_15_plot_data,
mapping = aes(x=per_capita_co2_emissions, y= country))+
geom_col()+
labs(title= "The top 15 and bottom per capita CO2 emissions",
subtitle = "for 1994",
x= NULL,
Y=NULL)